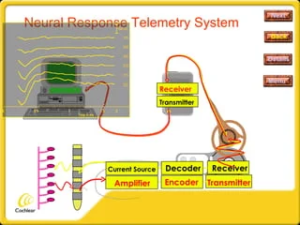
Neural Response Telemetry- NRT / NRI / ART
Electrically Evoked Compound Potentials – ( ECAP) NRT, ART & NRI
NRT, NRI, ART corresponds to the same thing—these are responses from auditory nerves that we receives when we stimulate the neurons by a Cochlear Implants.
Neural Response Telemetry -NRT,NRI or ART are sophisticated technology integral to the functioning of cochlear implants. It operates by generating a concise electrical impulse to stimulate the auditory nerve through one of the device’s electrodes. This brief stimulation is designed to trigger a neural response, a reaction that the implant’s telemetry system captures and documents.
Once this data is recorded, it is transmitted to the external device linked to the implant for thorough analysis. This step is crucial as it allows for the detailed examination of the neural response, which in turn reveals vital information about the health and performance of the auditory nerve. The telemetry data serves as a guide, enabling the clinician to tailor the cochlear implant fitting process to the individual needs of the patient.
These tests can be done during the Cochlear Implant surgery and at the time of switch ON and also during regular mapping sessions.
The feedback provided by NRT is invaluable in determining the optimal settings for the cochlear implant. By offering insights into how the auditory nerve responds to different levels of electrical stimulation, NRT helps clinicians fine-tune the device for maximum effectiveness. This personalized approach ensures each user receives the most beneficial and comfortable hearing experience possible, thus significantly improving their quality of life.
Benefits of ECAP –NRT, NRI , ART
Neural Response Telemetry (NRT) is a cutting-edge technology integral to the operation of cochlear implants. The numerous benefits it offers make it a crucial tool in audiological health care.
Objective Measurements—more definite
One of the paramount advantages of NRT is its capacity to yield objective measurements of neural responses. Unlike subjective assessments that rely on personal interpretations, NRT provides concrete, quantifiable data. This is particularly beneficial when dealing with populations incapable of providing reliable behavioural responses.
For instance, infants or individuals with cognitive impairments may struggle to accurately report their auditory experiences. With NRT, clinicians can bypass this challenge and obtain direct responses from the auditory nerve itself. By offering an objective methodology for assessing auditory nerve function, NRT bridges the gap between clinical needs and patient communication capabilities, leading to more accurate diagnostics and treatment plans.
Intraoperative Use
NRT’s benefits extend far beyond the clinic and into the operating room. Its intraoperative application has revolutionized cochlear implant surgeries. Audiologist can utilize NRT during the procedure to verify the implant’s functionality and the auditory nerve’s integrity immediately after insertion.
Audiologists can also guide surgeons regarding the surgical placement of the implant & if there are any glitches that can be rectified on the operating room with this objective tool
This real-time feedback is very important as it provides instantaneous confirmation of successful implantation. Consequently, it reduces uncertainties and risks associated with waiting for post-operative assessments. Such immediate validation offers peace of mind to the surgical team and reassurance to the patient’s family about the procedure’s success.
Personalized Mapping
Perhaps one of the most significant advantages of NRT is its facilitation of personalized mapping of cochlear implants. Every individual’s auditory system is unique, and a one-size-fits-all approach is not optimal for cochlear implant programming.
With the insights NRT provides into individual neural responses, clinicians can customize the ‘mapping’ or programming of the cochlear implant to suit each user’s specific needs. This personalized approach ensures that the device’s settings are optimally configured, leading to a more natural and comfortable listening experience for the user.
In turn, this can significantly improve outcomes, enhancing the patient’s auditory perception and overall quality of life. By tailoring each cochlear implant to the user, NRT allows for a level of individualized care that was previously unattainable, marking a significant advancement in audiological healthcare.
ECAP in Practice
Procedure
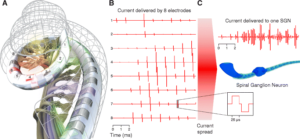
During an NRT session, the clinician will typically stimulate each electrode on the cochlear implant in turn, while recording the resulting neural responses. These responses are then analyzed to determine the minimum level of stimulation that produces a measurable response (the ‘threshold’) and the maximum comfortable level of stimulation.
Interpretation
The data obtained from NRT can be used to create a ‘map’ of the individual’s responses across the electrode array. This map can then be used to program the cochlear implant, with the goal of providing the most natural and comfortable listening experience possible.
Limitations
While NRT provides valuable information, it is not without limitations. For example, the measurements obtained are not direct recordings of neural activity but rather are derived from the combined response of many nerve fibres. Additionally, while NRT can provide information about the presence of a response, it does not provide information about the quality of the resulting auditory perception.
Future of ECAP -NRT, NRI , ART
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the potential for NRT. Advances in signal processing and data analysis techniques may allow for more detailed and accurate interpretation of NRT data. Furthermore, ongoing research into the relationship between NRT measurements and perceptual outcomes may enable even more personalized and effective cochlear implant programming in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Neural Response Telemetry is a powerful tool that allows for objective measurement of neural responses in cochlear implant users. By providing insight into individual neural responses, NRT enables more personalized and effective programming of the device, leading to improved outcomes for users. Despite its limitations, the future of NRT looks promising, with ongoing advancements and research paving the way for further improvements.